Field Effect Transistors
Part 3: CMOS
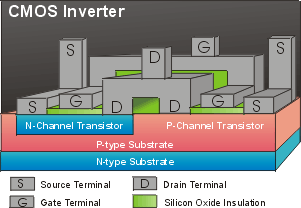
N-channel
and P-channel MOSFETs can be combined in pairs with a common gate,
a configuration known as Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
or CMOS. (Complementary means opposite.)
The
circuit shown here is an inverter: a circuit often used in digital
circuits in which the output voltage is the opposite of the input
voltage. Note that the gate terminals of both transistors are connected
together, as are the drain terminals.
In operation,
the source terminal of the N-channel transistor is connected to
the circuit common (negative), while the source terminal of the
P-channel transistor is connected to the positive supply voltage.
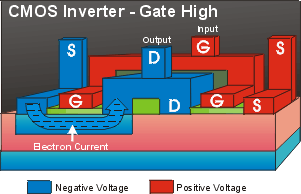
When the gate voltage is high current flows in the N-channel transistor,
but the P-channel transistor is off. This effectively creates a
short-circuit across the N-channel, so the output voltage is low
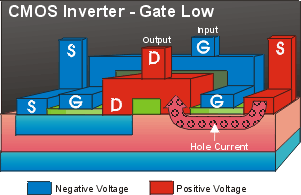
(the opposite of the input voltage). When the gate voltage is low,
the n-channel is shut off, but the P-channel transistor is turned
on, again creating a short circuit to the source terminal which
means that the output voltage is high.
Schematic
Diagram of CMOS Inverter (space) 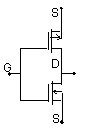

|

